Six Sigma

Course objectives:
- Understand the importance of process orientation
- Apply Six Sigma DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, Control) methodology
- Experience the negative effects of variation, see ways to measure and reduce it
- Find out different types of process factors: dependent, independent, controllable or not
- Ask the right questions to get to the root cause of problems
- Identify potential problems before they actually take place
- Apply this methodology and tools to one's own process with an improvement project
- IASSC Green Belt Lean Six Sigma Body of Knowledge
1. Define
- What is important? What is the problem?
- Project Scheduling
- Project charter: Goals, objectives, scope, justification, project participants
- Current status: go to Gemba
- Problem definition: SMART
- The voice of the customer: translate it to process specs
- Process map and flow chart: SIPOC
- Process Value Stream Map with MS Excel.
2. Measure
- What to measure?: Voice of the customer, Voice of the process, Business results
- Process metrics: Throughput, Yield, WIP, DPU, DPMO
- Test/ inspection: Coverage and First Pass Yield
- Operator and machine cycle times, Takt time and Lead time
- Data collection and validation
- Timestamp recording
- Basic statistics with Excel Data Analysis and Minitab
- Run charts and histograms
- Process capability: Cp, Cpk, sigma capability
- Attributes: Pareto
- Data stratification with Excel pivot tables
- Measurement system analysis
3. Analyze
- What to improve? Analyze the current process Value Stream Map
- Process inputs and process internal metrics (X)
- Source of defects, delays, waiting queues
- Bottleneck and waste identification
- Root cause: Cause and effect diagram
- IS - IS NOT methodology
- Test of hypothesis for variables and attributes
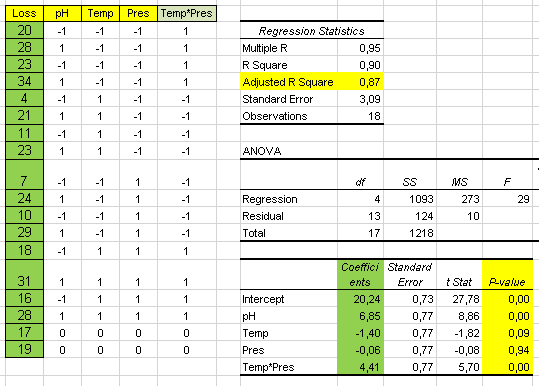
- Input variables (X) and output (Y): correlation and regression
- The Catapult exercise
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA)
- Sample size and confidence interval
4. Improve
- Process documentation: procedures and work instructions
- Prevention: Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
- Throughput, Work-In-Process and Lead Time
- Bottlenecks due to capacity, yield loss or variation
- Process impact of variation
- Process simulation with Excel
- Value Stream simulation
- 5S methodology
- Poka-Yokes (fail proof)
- Optimization with constraints: TOC
- Shared resource optimization: job scheduling
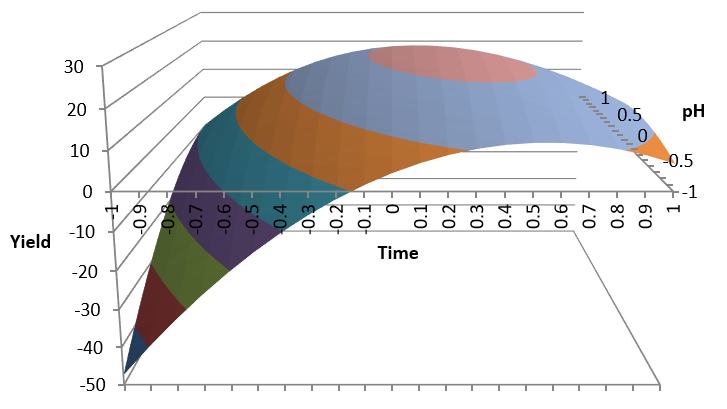
- Design of Experiments (DOE)
- DOE with Excel
- The Catapult exercise
- Response Surface Design of Experiments
5. Control
- Control plan design and implementation
- Statistical process control (SPC)
- Control charts for variables and attributes
- Western Electric rules: Interpretation
- Discrimination, repeatability, reproducibility
- Autocorrelation: how to manage it
- Real-time operator feedback
- Out of control: Who does what?
- Corrective actions: 8 discipline (8D) methodology

Comments
Post a Comment